
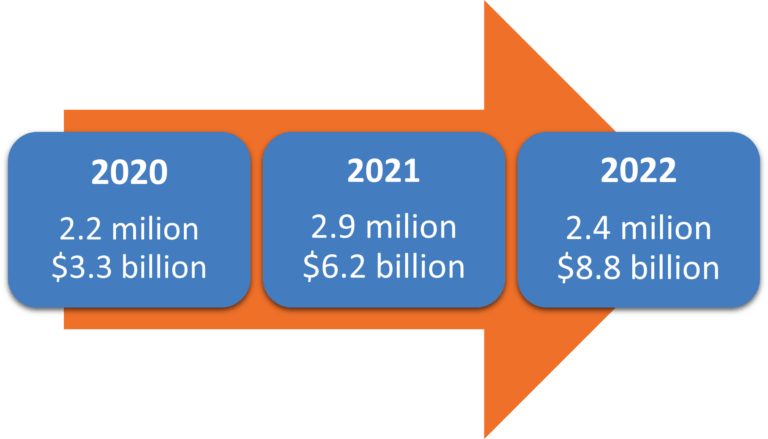
In the digital era, the significance of payment security and fraud prevention cannot be overstated. As the world becomes more interconnected and transactions increasingly move online, the risk of payment fraud has escalated. For instance, consumers lost over $8.8 billion to fraud in 2022 alone, as reported by the Federal Trade Commission. I will try to take you through the complexities of these challenges, offering an in-depth analysis of the several types of fraud, the importance of payment security, and the strategies that can be employed to prevent fraud. Furthermore, I will highlight the crucial roles of Know Your Customer (KYC) practices and ISO standards in strengthening payment security as well as the significance of regulatory compliance in maintaining a secure payment environment.
Payment fraud is a broad term that encompasses a wide array of fraudulent activities. These activities exploit vulnerabilities in payment systems to conduct illegal transactions. Card-not-present fraud, for instance, has been on the rise with the advent of online shopping. In this type of fraud, the fraudster uses stolen card information to make purchases online, over the phone, or through mail order. According to a report by Javelin Strategy & Research, card-not-present fraud is now 81% more common than point-of-sale fraud.
Phishing is a type of fraud where scammers impersonate legitimate organizations or individuals to trick people into revealing their personal or financial information. This information is then used to make fraudulent payments.
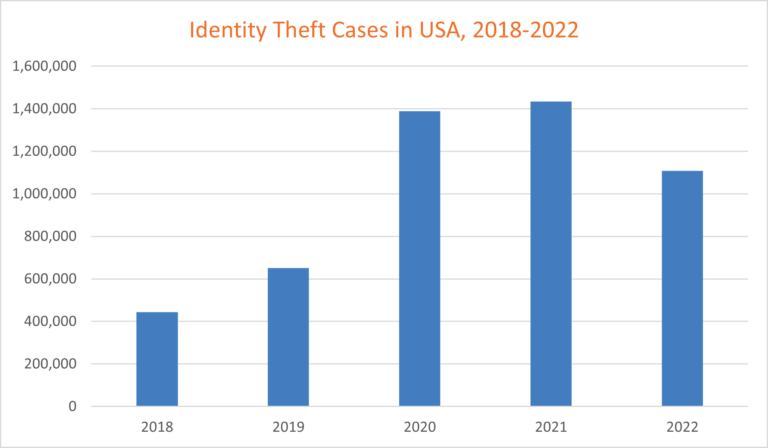
Identity theft is another common type of payment fraud. This occurs when a fraudster uses someone else’s personal information, such as their name, Social Security number, or credit card number, to commit fraud or other crimes. According to The Federal Trade Commission, the increase in the identity theft rate slowed down in 2021, and in 2022 the trend reversed due to multiple factors such as increased awareness and education, improved security measures, stricter regulations and enhanced fraud detection and prevention
Payment security is the cornerstone of any financial system. It is crucial for maintaining trust among users and protecting businesses and consumers from financial losses. A breach in payment security can lead to severe consequences, including financial damages, reputational harm, and loss of customer trust.
It is essential for businesses to implement robust payment security measures. By taking these steps, businesses can safeguard sensitive information, prevent fraudulent activities, and maintain the trust of their customers.
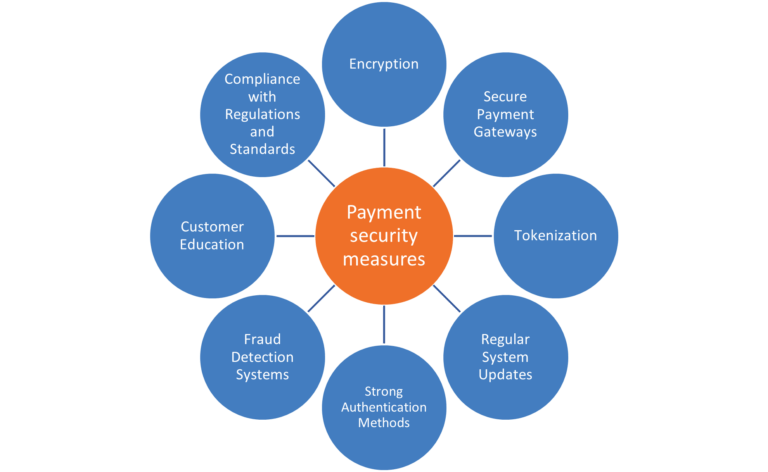
There are several measures that can be implemented to enhance payment security. Among these, encryption is a fundamental technique used by many companies, including giants like Amazon and PayPal, to protect customer data. Encryption works by converting payment information into a code to prevent unauthorized access. This means that even if a hacker intercepts the data, they would not be able to understand it without the decryption key.
Another important measure is tokenization. This involves replacing sensitive data with unique identification symbols, or “tokens,” that retain all the essential information about the data without compromising its security. This means that even if a fraudster manages to get hold of the token, they would not be able to reverse-engineer it to access the original data. Tokenization is particularly useful in protecting credit card information, as it allows businesses to conduct transactions without having to store sensitive card data.
Secure payment gateways are also crucial in enhancing payment security. These gateways act as a mediator between merchants and payment processors, facilitating the secure transfer of information. They use both encryption and tokenization to ensure that sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, are securely transmitted.
In addition to these measures, businesses also need to ensure that they have robust authentication processes in place. This could involve something as simple as requiring a password or PIN for transactions, or it could involve more complex methods like two-factor authentication or biometric authentication.
Regular system updates are crucial in maintaining payment security. This is because new threats and vulnerabilities are constantly emerging, and system updates often include patches for these vulnerabilities. By keeping their systems updated, businesses can protect themselves against the latest known threats.
Preventing payment fraud requires a multi-faceted approach. One of the key strategies in this regard is the use of fraud detection systems. These systems, often employed by credit card companies and banks, use advanced machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious activities and patterns. For instance, if a credit card is suddenly used in a location far from the user’s typical area of activity, or if there are several high-value transactions in quick succession, the system flags these as potentially fraudulent.
Strong authentication methods also play a crucial role in fraud prevention. These methods add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more pieces of evidence, or factors, to authenticate their identity. These factors could be something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a mobile device), or something the user is (like a fingerprint). By requiring multiple factors, it becomes significantly more difficult for fraudsters to gain unauthorized access to accounts.
Customer education is another essential strategy in preventing payment fraud. Many instances of fraud, such as phishing scams, rely on deceiving customers into providing sensitive information. By educating customers about the risks of fraud and how to recognize potential scams, businesses can empower their customers to protect themselves. This could involve providing information on their website, sending out regular email updates, or even hosting webinars or workshops.
In addition to these strategies, businesses should also ensure they are compliant with relevant regulations and standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and ISO 27001. Compliance with these regulations and standards not only helps prevent fraud but also protects businesses from legal consequences and penalties.
Know Your Customer (KYC) practices play a significant role in payment security. KYC involves verifying the identity of customers and assessing their risk profiles to prevent fraudulent activities. Banks and other financial institutions often use KYC procedures to ensure they are dealing with legitimate customers and reduce the risk of fraudulent transactions.
KYC procedures typically involve collecting and verifying information about a customer when they open an account or conduct financial transactions. This could include verifying the customer’s identity through government-issued documents, checking their name against lists of known parties involved in financial crime, and understanding the nature of the customer’s activities to ensure they are consistent with their business or occupation.
By implementing robust KYC procedures, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of becoming unwitting accomplices in money laundering or other fraudulent activities. This is because KYC procedures can help identify suspicious activities or inconsistencies that may indicate fraud. For instance, if a customer who typically makes small transactions suddenly starts making large, frequent transactions, this could be a red flag that warrants further investigation.
Moreover, KYC procedures are not just about preventing fraud; they are also a legal requirement in many jurisdictions. Regulatory bodies around the world require businesses, particularly those in the financial sector, to implement KYC procedures as part of their anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) efforts. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in hefty fines and penalties, not to mention the reputational damage that can come from being associated with financial crime.
ISO standards, developed by the International Organization for Standardization, provide guidelines and best practices for various aspects of payment security. Among these, ISO 27001 is particularly relevant. This standard provides guidelines for information security management systems (ISMS), outlining the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an ISMS.
Companies like Microsoft and IBM are ISO 27001 certified, demonstrating their commitment to implementing appropriate security controls and measures. The certification process involves a two-stage audit conducted by an independent, accredited certification body. The first stage assesses whether the company’s ISMS meets the requirements of the standard, while the second stage verifies that the company is effectively implementing its ISMS.
Compliance with ISO 27001 ensures that businesses have implemented appropriate security controls and measures. These controls and measures are based on a risk assessment that considers the specific threats and vulnerabilities that the business faces. This means that the security measures implemented by an ISO 27001 certified company are tailored to its specific needs and risks, providing a robust and effective defence against potential security breaches.
Moreover, ISO 27001 certification provides a level of assurance to customers, partners, and stakeholders that the company takes information security seriously. It demonstrates that the company has implemented a systematic approach to managing sensitive information and ensuring its security, confidentiality, and integrity.
Regulatory compliance is a key aspect of payment security. It involves adhering to laws, regulations, guidelines, and specifications relevant to a business’s operations. In the context of payment security, this includes compliance with KYC regulations, ISO standards, and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
KYC regulations, as discussed earlier, require businesses to verify the identity of their customers and assess their risk profiles. Compliance with these regulations helps prevent fraudulent activities and is a legal requirement in many jurisdictions. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and penalties, not to mention the reputational damage that can come from being associated with financial crime.
ISO standards, particularly ISO 27001, provide guidelines for information security management systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that businesses have implemented appropriate security controls and measures, providing a robust defence against potential security breaches. Moreover, ISO 27001 certification enhances a business’s reputation and credibility, demonstrating to customers, partners, and stakeholders that the business takes information security seriously.
The PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. The PCI DSS is enforced by the major credit card companies and applies to all businesses that handle credit card transactions, regardless of their size or the number of transactions they process. Companies that fail to comply with PCI DSS can face fines, along with potential lawsuits and reputational damage.
In the face of escalating payment fraud, the importance of robust payment security measures, fraud prevention strategies, and regulatory compliance is paramount. Understanding the several types of fraud, implementing secure payment measures, and employing fraud prevention strategies are all crucial steps in safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining customer trust. The roles of Know Your Customer practices and ISO standards are also significant in enhancing payment security, helping businesses verify customer identities, assess risk profiles, and implement appropriate security controls. Furthermore, regulatory compliance, including adherence to KYC regulations, ISO standards, and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, is essential in not only preventing fraud but also protecting businesses from legal consequences and penalties. In an increasingly digital world, these comprehensive approaches to payment security are not just beneficial — they are necessary to protect businesses and their customers from the potential devastation of financial crime.
As experts in payment security and fraud prevention, Brickendon can support our Customers by offering comprehensive solutions and guidance to protect their financial transactions and assure their reputation unharmed. We stay on top of the latest trends and emerging threats in payment fraud to provide timely advice and recommendations.
Explore the latest Insights from Brickendon and ensure that your organisation is prepared.
Sources: